Academic Publishing and Fairness: A Game-Theoretic Model of Peer-Review Bias
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
A free and fair economy: definition, existence and uniqueness
2.1 A free economy
2.2 A free and fair economy
-
Equilibrium existence in a free and fair economy
3.1 A free and fair economy as a strategic form game
3.2 Existence of an equilibrium
-
Equilibrium efficiency in a free and fair economy
-
A free economy with social justice and inclusion
5.1 Equilibrium existence and efficiency in a free economy with social justice
5.2 Choosing a reference point to achieve equilibrium efficiency
-
Some applications
6.1 Teamwork: surplus distribution in a firm
6.2 Contagion and self-enforcing lockdown in a networked economy
6.3 Bias in academic publishing
6.4 Exchange economies
-
Contributions to the closely related literature
-
Conclusion and References
Appendix
6.3 Bias in academic publishing

\ 
\ 
\ 
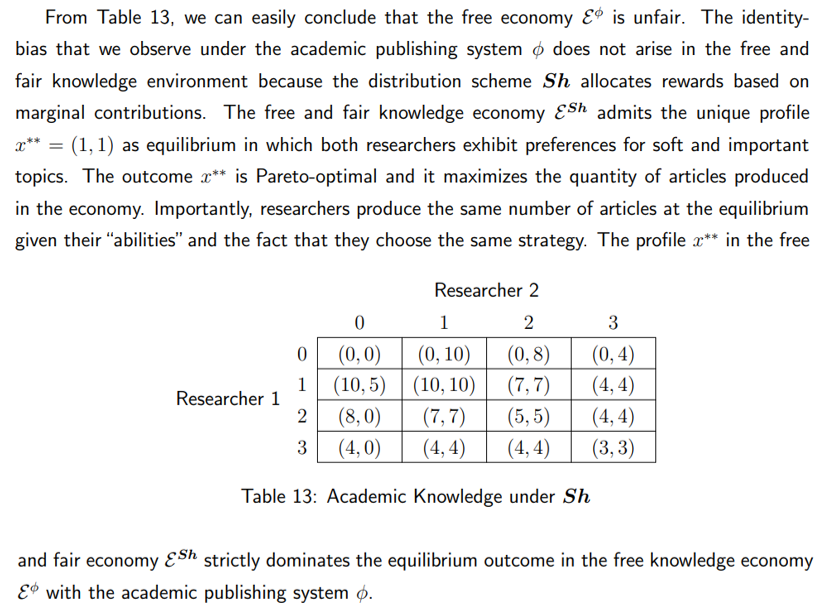
\ Well, it is straightforward to show that the researchers are symmetric under the knowledge function f. Using Anonymity and the other principles of merit-based justice, Table 13 below describes the allocation of academic articles under the allocation Sh.
\ 
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Ghislain H. Demeze-Jouatsa, Center for Mathematical Economics, University of Bielefeld (demeze jouatsa@uni-bielefeld.de);
(2) Roland Pongou, Department of Economics, University of Ottawa (rpongou@uottawa.ca);
(3) Jean-Baptiste Tondji, Department of Economics and Finance, The University of Texas Rio Grande Valley (jeanbaptiste.tondji@utrgv.edu).
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::
[10] Tough the trade-off between the two quality dimensions can be viewed as a rational decision, the consequences can be detrimental to economics, as a discipline and profession. For instance, some general interest journals suffer from the “incest factor” [Heckman et al., 2017], and Akerlof [2020] shows that the tendency of rewarding “hard” topics versus“ soft ”topics in economics results in “sins of omissions” where issues that are relevant to the literature and can not be approached in a “hard” way are ignored.
\ 
You May Also Like
Crypto execs met with US lawmakers to discuss Bitcoin reserve, market structure bills
Lawmakers in the US House of Representatives and Senate met with cryptocurrency industry leaders in three separate roundtable events this week. Members of the US Congress met with key figures in the cryptocurrency industry to discuss issues and potential laws related to the establishment of a strategic Bitcoin reserve and a market structure.On Tuesday, a group of lawmakers that included Alaska Representative Nick Begich and Ohio Senator Bernie Moreno met with Strategy co-founder Michael Saylor and others in a roundtable event regarding the BITCOIN Act, a bill to establish a strategic Bitcoin (BTC) reserve. The discussion was hosted by the advocacy organization Digital Chamber and its affiliates, the Digital Power Network and Bitcoin Treasury Council.“Legislators and the executives at yesterday’s roundtable agree, there is a need [for] a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve law to ensure its longevity for America’s financial future,” Hailey Miller, director of government affairs and public policy at Digital Power Network, told Cointelegraph. “Most attendees are looking for next steps, which may mean including the SBR within the broader policy frameworks already advancing.“Read more

Coinbase CEO: Coinbase embedded wallet now supports login via Google, Apple, and X.
